The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) has issued a new final rule regarding the salary threshold for determining whether employees are exempt from federal overtime pay requirements. The threshold is slated to jump 65% from its current level by 2025 and is expected to make four million additional workers eligible for overtime pay.
On the same day the overtime rule was announced, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) approved a final rule prohibiting most noncompete agreements with employees, with similarly far-reaching implications for many employers. Both regulations could be changed by court challenges, but here’s what you need to know for now.
The overtime rule
Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), so-called nonexempt workers are entitled to overtime pay at a rate of 1.5 times their regular pay rate for hours worked per week that exceed 40. Employees are exempt from the overtime requirements if they satisfy three tests:
- Salary basis test. The employee is paid a predetermined and fixed salary that isn’t subject to reduction due to variations in the quality or quantity of his or her work.
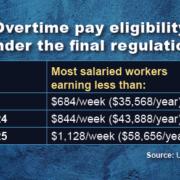
- Salary level test. The salary isn’t less than a specific amount, or threshold (currently, $684 per week or $35,568 per year).
- Duties test. The employee primarily performs executive, administrative or professional duties.
The new rule focuses on the salary level test and will increase the threshold in two steps. Starting on July 1, 2024, most salaried workers who earn less than $844 per week will be eligible for overtime. On January 1, 2025, the threshold will climb further, to $1,128 per week.
The rule also will increase the total compensation requirement for highly compensated employees (HCEs). HCEs are subject to a more relaxed duties test than employees earning less. They need only “customarily and regularly” perform at least one of the duties of an exempt executive, administrative or professional employee, as opposed to primarily performing such duties.
This looser test currently applies to HCEs who perform office or nonmanual work and earn total compensation (including bonuses, commissions and certain benefits) of at least $107,432 per year. The compensation threshold will move up to $132,964 per year on July 1, and to $151,164 on January 1, 2025.
The final rule also includes a mechanism to update the salary thresholds every three years. Updates will reflect current earnings data from the most recent available four quarters from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. The rule also permits the DOL to temporarily delay a scheduled update when warranted by unforeseen economic or other conditions. Updated thresholds will be published at least 150 days before they take effect.
Plan your approach
With the first effective date right around the corner, employers should review their employees’ salaries to identify those affected — that is, those whose salaries meet or exceed the current level but fall below the new thresholds. For employees who are on the bubble under the new thresholds, employers might want to increase their salaries to retain their exempt status. Alternatively, employers may want to reduce or eliminate overtime hours or simply pay the proper amount of overtime to these employees. Or they can reduce an employee’s salary to offset new overtime pay.
Remember, too, that exempt employees also must satisfy the applicable duties test (which varies depending on whether the exemption is for an executive, professional or administrative role). An employee whose salary exceeds the threshold but doesn’t primarily engage in the applicable duties isn’t exempt.
Obviously, depending on the selected approach, budgets may require adjustments. If some employees will be reclassified as nonexempt, employers may need to provide training to employees and supervisors on new timekeeping requirements and place restrictions on off-the-clock work.
Be aware that business groups have promised to file lawsuits to block the new rule, as they succeeded in doing with a similar rule promulgated in 2016. Also, the U.S. Supreme Court has taken a skeptical eye to administrative rulemaking in recent years. So it makes sense to proceed with caution. Bear in mind, too, that some employers also are subject to state and local wage and hour laws with more stringent standards for exempt status.
The noncompete ban
The new rule from the FTC bans most noncompete agreements nationwide (which will conflict with some state laws). In addition, existing noncompetes for most workers will no longer be enforceable after the rule becomes effective, 120 days after it’s published in the Federal Register. The rule is projected to affect 30 million workers. However, it doesn’t apply to certain noncompete agreements and those entered into as part of the sale of a business.
The rule includes an exception for existing noncompetes with “senior executives,” defined as workers earning more than $151,164 annually who are in policy-making positions. Policy-making positions include:
- A business’s president,
- A chief executive officer or equivalent,
- Any other officer who has policy making authority, and
- Any other natural person who has policy making authority similar to an officer with such authority.
Note that employers can’t enter new noncompetes with senior executives.
Unlike the proposed rule issued for public comment in January 2023, the final rule doesn’t require employers to legally modify existing noncompetes by formally rescinding them. Instead, they must only provide notice to workers bound by existing agreements — other than senior executives — that they won’t enforce such agreements against the workers. The rule includes model language that employers can use to provide notice.
A lawsuit was filed in a Texas federal court shortly after the FTC voted on the final rule, arguing the FTC doesn’t have the statutory authority to issue the rule. The U.S. Chamber of Commerce also subsequently filed a court challenge to block the noncompete ban.
More to come
Whether either of these rules will eventually become effective as written remains to be seen. Judicial intervention or a potential swing in federal political power could mean they land in the dustbin of history before taking effect — or shortly thereafter. We’ll keep you up to date on the latest news regarding these two rules.
© 2024